What is a Steering Committee?
A steering committee is an advisory body that plays a significant role in guiding and managing the direction, scope, budget, and timelines of a project or organization. It comprises senior stakeholders, experts, and authority figures who bring diverse perspectives and expertise to ensure the successful completion of projects.
Key Functions of a Steering Committee
- Providing Advice and Direction: Steering committee members use their expertise to offer recommendations that steer the project towards its goals. They define measurable and trackable objectives to ensure the project remains on course.
- Setting Project Timeline and Budget: The committee establishes milestones and deadlines, managing the project budget to keep it aligned with the timeline and financial constraints.
- Monitoring Project Quality: They identify quality standards, audit them regularly, and track results to ensure the project meets its goals and legal safety requirements.
- Evaluating and Monitoring Risks: Steering committees proactively identify potential risks, assess their likelihood and impact, and develop plans to mitigate them.
- Defining Project Outcomes: They outline specific, measurable, and meaningful outcomes to ensure the project achieves its intended impact.
Roles and Responsibilities of Steering Committee Members
Composition of the Steering Committee
Steering committees typically include senior managers, executives, key external stakeholders, and subject matter experts. The composition varies depending on the project’s purpose, but it generally aims to cover all functions under its purview.
Key Roles
- Chairperson: Elected to lead the committee, ensuring impartiality and effective governance.
- Senior Stakeholders: Key decision-makers who bring authority and expertise to the project.
- Subject Matter Experts: Individuals with specialized knowledge relevant to the project’s goals.
Responsibilities
- Advocating for Projects: They promote initiatives and projects within the organization.
- Strategic Guidance: Offering advice on budgeting, resource allocation, and strategic direction.
- Approving Plans and Changes: Reviewing and endorsing project plans, timelines, and budget adjustments.
- Resolving Conflicts: Mediating disputes and providing solutions to project-related issues.
- Risk Management: Identifying, monitoring, and addressing potential risks to the project.
- Ensuring Quality: Keeping an eye on project quality and making necessary adjustments.
How to Run an Effective Steering Committee
Clear Objectives and Organized Agenda
To be effective, a steering committee must have well-defined objectives and a structured agenda. This ensures that meetings are productive and focused on achieving the project’s goals.
Open Dialogue and Diverse Perspectives
Encouraging open dialogue and including diverse perspectives helps in considering all opinions and making well-rounded decisions.
Utilizing Business Intelligence (BI)
Using BI tools to gather and analyze data allows the committee to make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information. This is crucial for tracking project progress and identifying areas for improvement.

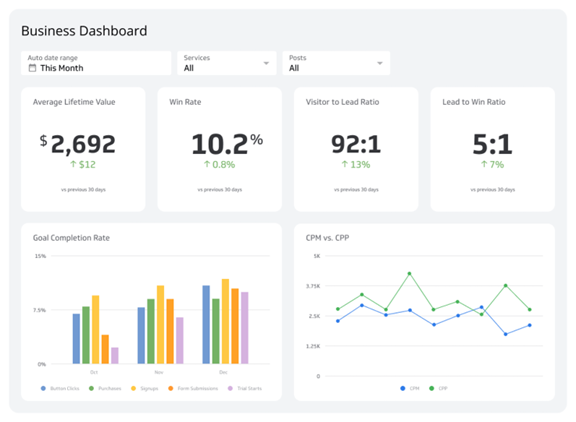
Example of Effective Steering Committee Use
Consider a project where the steering committee uses a BI dashboard to monitor progress. The dashboard shows the status of various tasks, highlighting areas experiencing delays. With this data, the committee can quickly address issues, reallocate resources, and keep the project on track.
Conclusion
A well-functioning steering committee is essential for the successful management of projects and organizational goals. By providing strategic direction, managing risks, ensuring quality, and utilizing accurate data, steering committees can significantly enhance the value and success of any project.
Steering committees bridge the gap between project teams and organizational leadership, ensuring that projects are completed efficiently and effectively. Understanding their roles and responsibilities is crucial for anyone involved in project management or organizational leadership.



